PESTLE ANALYSIS
The PEST/ PESTLE/ PESTEL analysis is a tool for analysing a business’s macro environment. It examines the organisation’s political, economic, sociological, technological, legal, and environmental aspects (Achinas, 2019). It provides an overview of the entire context from many perspectives that one might want to verify and monitor when deliberating over an idea or plan.

Political factors
These factors entails the government’s ability to affect the economy or a specific sector. When governments apply new taxes or duties, for instance, businesses may have to rethink how they generate income as a result (Shtal et al., 2018). A government’s tax policies, Fiscal policy, trade tariffs, etc., that it imposes at the beginning of its fiscal year can have a significant impact on the business environment.
Economic factors
These aspects are the driving forces behind an economy’s performance, which has reverberating consequences on businesses (Shtal et al., 2018). For instance, if inflation were to rise in any country, this would have an effect on how much businesses charged for their goods and services. Not only would it impact the demand and supply patterns for that economy, but it would also affect consumers’ purchasing power. The interest rates, economic growth patterns, inflation rate, foreign exchange rates, etc. are all examples of economic factors.
Social factors
These aspects analyse the market’s societal context and its driving forces, such as demographics, consumer preferences, and cultural trends (Shtal et al., 2018).
Technological factors
These elements relate to technological developments that may have positive or negative effects on business and economic activity (Shtal et al., 2018). This pertains to the degree to which a market is automated, invests in Research & development activities, and is generally aware of technical advancements.
Legal factors
There are internal and external aspects to these factors. Both the legal climate in a given country and the internal policies of individual businesses can have an impact on its success. Analysis from a legal perspective considers both of these perspectives and plans accordingly (Shtal et al., 2018). For instance, safety standards, consumer laws, labour laws, etc.
Environmental factors
Anything that is affected by or is a result of the external environment is included here. Climate, weather, geography, worldwide changes in climate, environmental offsets, etc. are all examples of factors that might be included in an examination of the business’s environmental context (Shtal et al., 2018).

Porter’s five forces
Developed by Professor Michael E. Porter set the Five Forces model is used to analyse the competitive environment in terms of five key forces that impact a company’s profitability and influence its strategy. It is a micro-environment framework that attempts to analyse the level of competition within an industry (Gray, 2021). The Five Forces include – three forces from ‘horizontal’ competition: the threat of substitute products or services, the threat of established rivals, and the threat of new entrants; and two forces from ‘vertical’ competition: the bargaining power of suppliers and the bargaining power of customers. Porter’s Five Forces is considered a macro tool in business analytics – it looks at the industry’s economy as a whole (Gray, 2021).
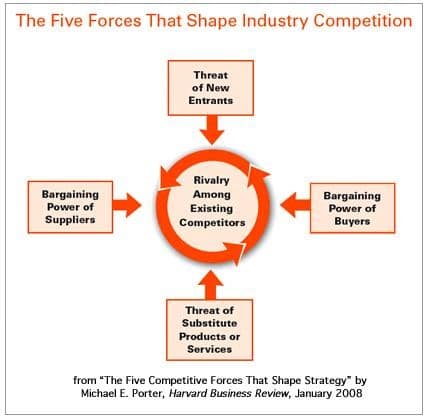
- Competitive rivalry: The level of market competitiveness is investigated by this force. It takes into account the variety and capabilities of the existing competition.
- The bargaining power of suppliers: This factor considers the supplier’s bargaining position and the extent to which it can raise prices, so cutting into the company’s profit margins (Bruijl & Gerard, 2018).
- The bargaining power of customers: This force analyses customer influence and its impact on costs and product quality. If there are few buyers but many vendors, the buyers will have more power. This is because it is simple for the buyers to switch providers (Bruijl & Gerard, 2018). Alternatively, consumers have less purchasing power when they make infrequent purchases of a unique product.
- The threat of new entrants: This force takes into account the level of difficulty (or simplicity) with which new competitors can enter the market. When entry barriers are low, existing companies are more vulnerable to seeing their market share eroded by new entrants.
- The threat of substitute products or services: This force investigates the ease with which customers can move to a competitor’s product or service (Bruijl & Gerard, 2018). It looks at how many rivals there are, how their prices and quality stack up against the company under review, and how much money those rivals are making, to gauge whether or not the under review can lower their own prices more.




